Key Insights into Construction Machinery Castings: Products, Materials, and Standards
2024-12-09 13:40:30 hits:0
Construction Machinery Castings refer to metal castings used in construction machinery equipment. These castings are typically required to withstand high strength, high wear, and complex working environments, demanding high-quality and performance standards. Below is an introduction to the main products, raw material requirements for pig iron, and related standards:
Main Products
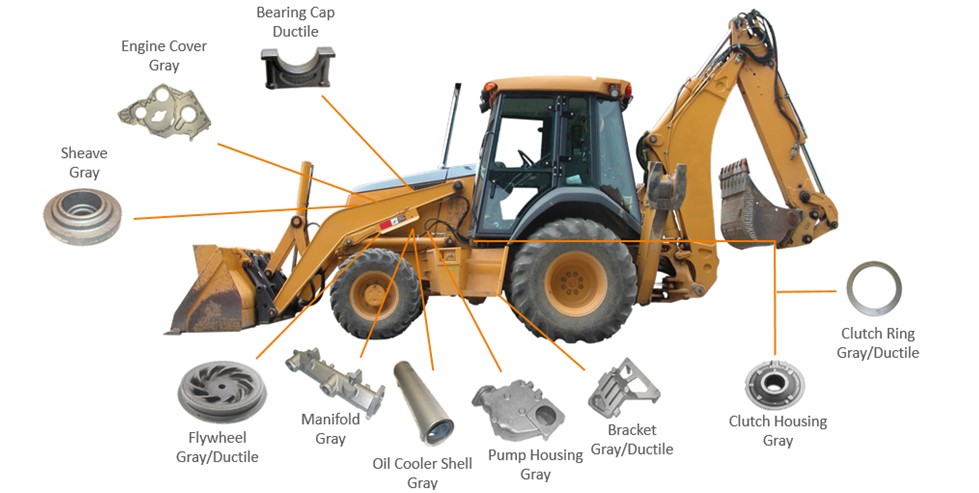
Excavator Components
- Buckets
- Bucket Teeth
- Bucket Edge Plates
- Bucket Connecting Parts
Loader Components
- Buckets
- Rocker Arms
- Articulated Joints
Bulldozer Components
- Track Links
- Drive Wheels
- Support Rollers
- Carrier Rollers
Other Construction Machinery Parts
- Crane Hooks
- Gearbox Housings
- Brake Discs and Brake Drums
Requirements for Pig Iron as Raw Material
Chemical Composition
- Carbon Content: Generally 2.5%–3.6%, ensuring good casting performance.
- Silicon Content: Typically 1.0%–2.0%, improving fluidity and casting toughness.
- Sulfur and Phosphorus Content: Preferably below 0.08% and 0.05%, respectively, to reduce brittleness in castings.
Mechanical Properties
- Pig iron must have good strength and ductility to ensure castings can withstand complex working environments.
Impurity Control
- Should contain low levels of non-metallic inclusions (e.g., oxides, silicates).
Wear Resistance
- For components requiring high wear resistance (e.g., bucket teeth), appropriate amounts of alloying elements such as chromium, manganese, or vanadium can be added.
Product Standards
International Standards
- ASTM A532 (High Chromium Cast Iron): Applicable to wear-resistant castings.
- ASTM A48 (Gray Cast Iron): For general-purpose mechanical castings.
- ISO 1083 (Ductile Cast Iron): Emphasizes toughness and impact resistance.
Chinese Standards
- GB/T 9439-2010 (Gray Iron Castings)
- GB/T 1348-2009 (Ductile Iron Castings)
- GB/T 11352-2020 (Carbon Steel Castings for General Engineering)
Industry Standards
- Customized specifications may exist depending on specific machinery industries (e.g., construction machinery, building equipment).
Additional Considerations
Quality Control
- Strictly monitor the melting process's temperature and chemical composition.
- Conduct non-destructive testing (e.g., ultrasonic, X-ray) to ensure no internal defects in the castings.
Heat Treatment
- Apply heat treatments such as normalizing, quenching, or tempering to certain castings (e.g., high-wear components) to enhance strength and toughness.
Surface Coating
- Casting surfaces are typically coated with anti-rust paint to enhance corrosion resistance.

 en
en  fra
fra  de
de  ru
ru  gle
gle  th
th  ara
ara  it
it  jp
jp  kor
kor  zh
zh