The Competitiveness of Chinese Castings Export
2024-12-06 15:43:39 hits:0
1. Current Status of Chinese Castings Export
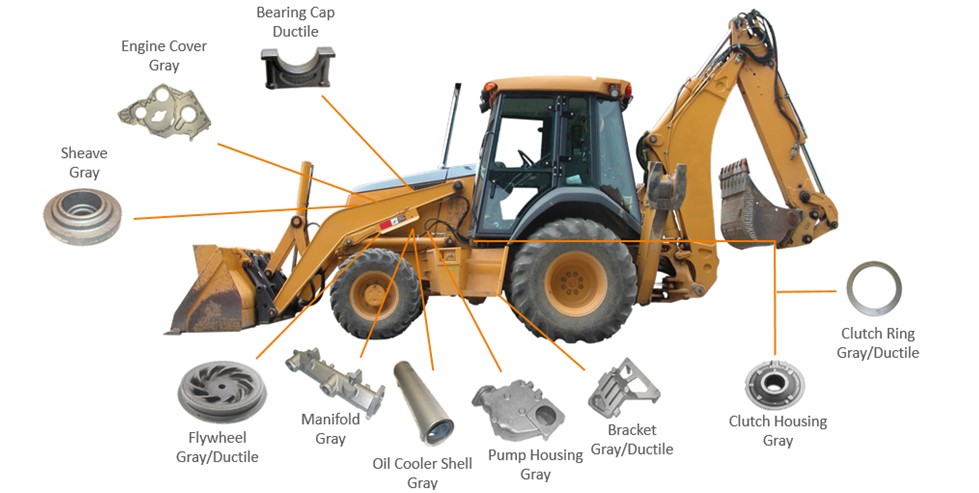
1.1 Export Volume
China is the world's largest producer and exporter of castings, contributing about 45%-50% of the global output annually.
According to the China Foundry Association, castings exports account for approximately 10%-15% of China's total production, covering automotive parts, machinery components, pipeline fittings, and rail transit equipment.
1.2 Major Export Regions
North America: The U.S. and Canada demand Chinese castings mainly for automotive components, construction machinery, and energy equipment, especially high-strength cast iron and aluminum castings.
Europe: Germany, the UK, and France are key markets, particularly for high-precision and high-value-added castings.
Asia and Emerging Markets: Southeast Asia, India, and the Middle East are among the fastest-growing markets.
Africa: Primarily focused on castings for infrastructure projects.
1.3 Export Product Types
Gray iron, ductile iron, and aluminum alloy castings dominate the market.
With the global trend toward lightweight materials, the export share of stainless steel and high-performance aluminum alloy castings is gradually increasing.
2. Advantages of Chinese Castings Export
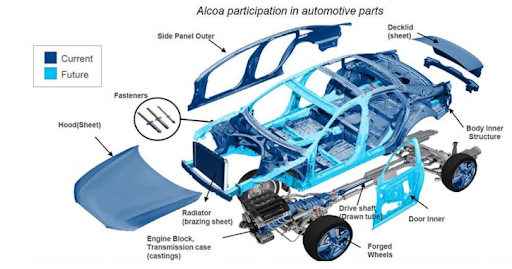
2.1 Quality Advantages
China’s casting quality has transformed from being traditionally perceived as "low-cost and average quality" to "high cost-performance and high quality."
1. Modernized Technical Equipment
Advanced technologies like automated pouring, robotic coating, and 3D-printed molds significantly enhance precision and consistency.
Many factories are equipped with state-of-the-art machines such as German spectrometers and U.S. coordinate measuring machines.
2. High Standard Quality Systems
Many export enterprises are certified under ISO 9001, ISO/TS 16949, and EN 124 standards.
Stringent inspection and testing, including metallographic analysis, non-destructive testing (X-ray, ultrasonic), and mechanical performance evaluation, are implemented.
3. Innovation Capability
China is actively developing new materials (e.g., high-temperature alloys and lightweight composites) and complex high-precision castings for sectors like aerospace and medical equipment.
2.2 Cost Advantages

1. Labor Costs
Despite rising labor costs, China still has lower production and labor expenses compared to developed countries, with an abundant supply of skilled workers and technical talents.
2. Material Costs
China possesses the world's largest steel production capacity, ensuring a stable and competitive raw material supply.
Auxiliary materials like foundry sand and coatings are readily available, further reducing production costs.
3. Economies of Scale
Large foundries optimize production processes and adopt automation technologies to lower per-unit costs.
2.3 Production Capacity and Efficiency
1. World-Leading Production Capacity
With tens of thousands of foundries, China offers extensive capacity ranging from small-scale plants producing a few thousand tons annually to large-scale enterprises with millions of tons of output.
2. Flexible Production Systems
Capable of meeting both high-volume and customized, high-precision orders.
Fast mold development and production switching reduce delivery times.
3. Process Innovation
Techniques such as lost foam casting, precision casting, and die casting minimize machining allowances and energy consumption while improving surface quality.
2.4 Service and Supply Chain Advantages

1. End-to-End Services
Chinese casting exporters typically offer integrated services, including design, mold manufacturing, casting, post-processing (e.g., machining, heat treatment), packaging, and transportation, making client communication seamless.
2. Logistics Efficiency
Leveraging China’s advanced port and logistics networks ensures fast delivery worldwide.
The "Belt and Road" Initiative has further facilitated trade with participating countries.

 en
en  fra
fra  de
de  ru
ru  gle
gle  th
th  ara
ara  it
it  jp
jp  kor
kor  zh
zh 


