What Problems Occur in Sand Casting if Sulfur Content is Too High?
2024-12-04 13:42:59 hits:0

Sand casting is a widely used metal forming process in modern industry, but the quality of castings is often influenced by many factors. Among them, sulfur content is a critical parameter that cannot be overlooked. Sulfur, as an impurity element, can negatively impact the performance and structure of castings if not properly controlled during the casting process. This article will analyze the specific effects of high sulfur content in sand casting and explore the underlying causes and potential solutions.
Main Problems Caused by High Sulfur Content
1.Graphite Degradation (Applicable to Ductile Iron and Gray Cast Iron)
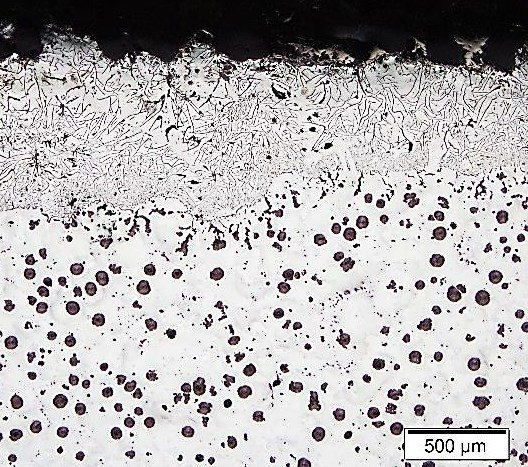
In ductile iron and gray cast iron, sulfur interferes with the normal nucleation and growth of graphite, leading to changes in the graphite morphology:
- For ductile iron, high sulfur content suppresses the effect of nodulizing agents (such as magnesium), causing the graphite to form in irregular shapes, such as flake or vermicular forms, rather than the ideal spheroidal shape. This significantly reduces the material’s strength and toughness.
- For gray cast iron, high sulfur content causes uneven growth of flake graphite and even rough edges, affecting the material’s thermal conductivity and mechanical properties.
2.Increased Susceptibility to Hot Cracking
Sulfur reduces the fluidity of the molten metal and its ability to shrink during solidification, which can lead to the formation of hot cracks within the casting.This issue is particularly prominent in complex structures or castings with varying wall thicknesses.
3.Formation of Sulfide Inclusions
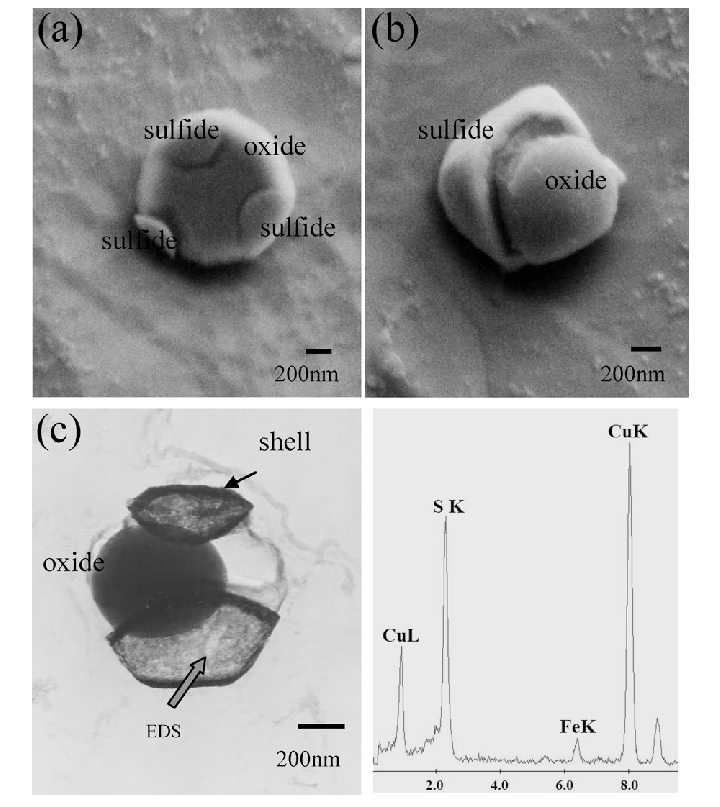
High sulfur content reacts with other elements in the metal, such as iron and manganese, to form sulfide inclusions. These inclusions create weak interfaces in the casting, reducing mechanical properties like tensile strength and toughness.
4.Surface Quality Issues
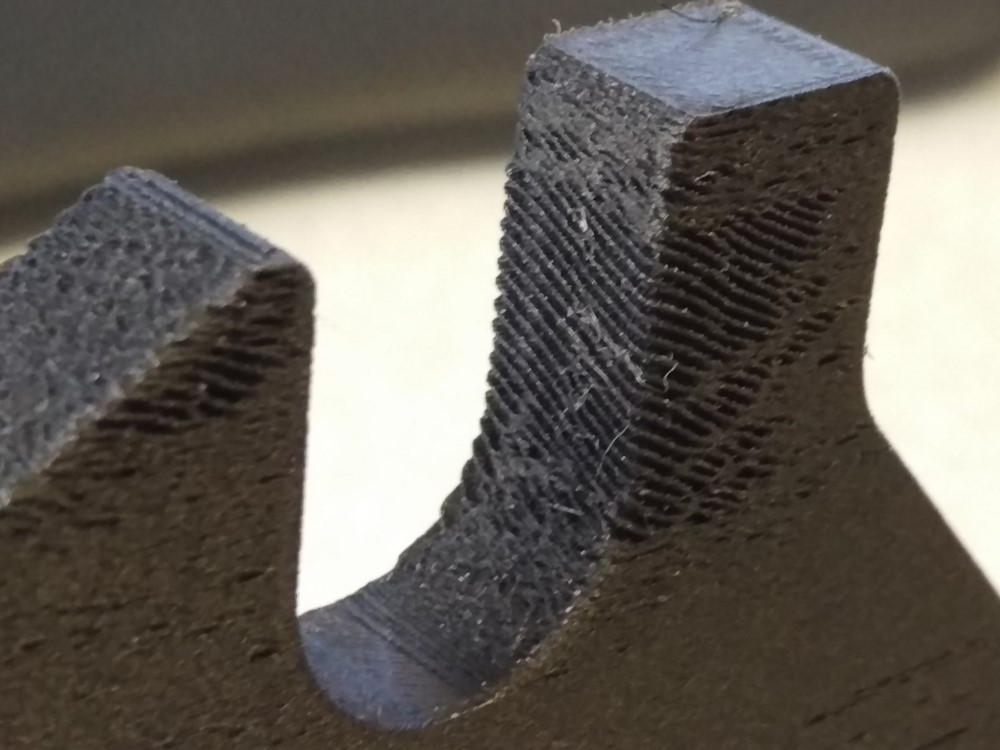
Excessive sulfur can lead to rough surface defects or pinholes in the casting. This occurs when sulfur gas trapped during cooling fails to escape from the casting surface.
5.Increased Brittleness
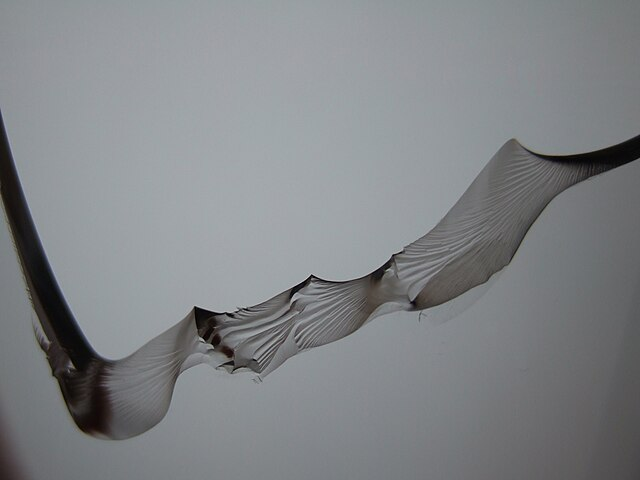

Sulfur tends to segregate along grain boundaries, forming low-melting-point sulfide phases that reduce the casting’s impact resistance and ductility, making it more brittle and prone to fracture.
Mechanism of Impact
The effects of sulfur mainly manifest in the following ways:
1.Chemical Reactions:
Sulfur reacts with other elements in the metal (such as magnesium, iron, and manganese) to form undesirable phases, such as magnesium sulfide and iron sulfide.
2.Gas Effects:
At high temperatures, sulfur exists in the form of hydrogen sulfide gas, which affects the fluidity of the molten metal and the filling of the mold cavity.
3.Grain Boundary Segregation:
Sulfur tends to accumulate at grain boundaries, altering the strength and properties of the grain boundaries, thus reducing the overall material performance.
Solutions
1.Strict Control of Raw Material Quality

Choose raw materials with low sulfur content and conduct composition testing before charging the furnace.
2.Use of Desulfurizing Agents

Add suitable desulfurizing agents, such as magnesium, calcium, or barium, during the smelting process to reduce sulfur residue.
3.Optimization of Melting Process
Increase the melting temperature and ensure uniform stirring to prevent the formation of sulfide inclusions.
4.Use of Improved Sand Mold Materials
Ensure that the mold sand mixture is appropriately proportioned to prevent sulfur-containing gases from being released from the mold and affecting the casting quality.
5.Online Monitoring and Analysis

Use techniques such as spectroscopy to monitor sulfur content in real time, ensuring it remains within acceptable limits.
In sand casting, sulfur is a "double-edged sword." While it may help improve certain properties in some specialized processes, high sulfur content generally causes serious issues. By strictly controlling raw materials, optimizing processes, and conducting real-time monitoring, foundries can effectively mitigate the adverse effects of sulfur and improve casting quality. This not only helps meet customer demands for high-performance products but also enhances the competitiveness of the enterprise in the market.

 en
en  fra
fra  de
de  ru
ru  gle
gle  th
th  ara
ara  it
it  jp
jp  kor
kor  zh
zh 


