How to Choose the Right Cast Iron Casting Process?
2024-11-21 09:48:31 hits:0
Cast iron is a critical material in industrial manufacturing, valued for its excellent mechanical properties, heat resistance, and corrosion resistance. However, selecting the appropriate casting process based on specific application needs and production conditions is essential. A well-chosen casting process can improve product quality, reduce production costs, and enhance manufacturing efficiency. In this article, I will discuss the common processes of cast iron casting and their applicable scenarios to help readers understand how to choose the appropriate casting method.
1.Common Cast Iron Casting Processes and Their Features
The main casting processes for cast iron include sand casting, lost foam casting, precision casting, and pressure casting. Below are the characteristics and applications of these methods:
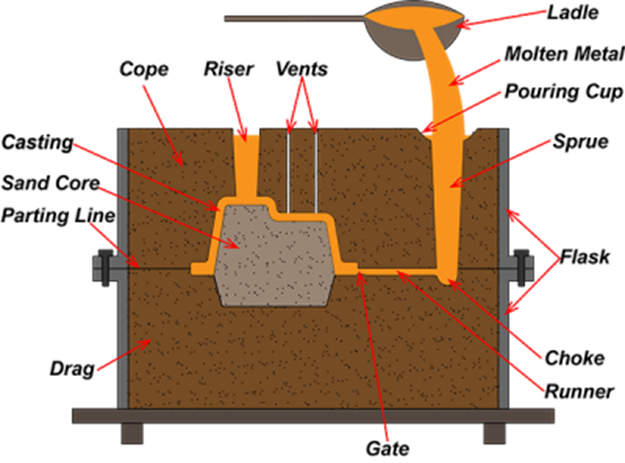
1.1 sand casting
Sand casting is one of the oldest and most widely used casting methods. It is cost-effective and versatile, suitable for producing a wide range of cast iron products, from small components to large structures
- Advantages:
Ideal for complex structures and large workpieces, with high material utilization. - Disadvantages: Poor surface quality, low dimensional accuracy, and significant post-processing requirements.
- Applications:Examples include pipe fittings, machine tool bases, and pump housings.
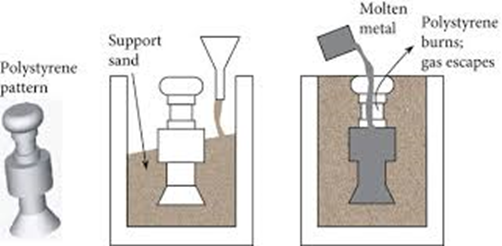
1.2 Lost Foam Casting
Lost foam casting uses foam models instead of traditional sand molds. The model vaporizes when molten metal is poured in. This process offers high flexibility in production.
- Advantages: No need for mold parting, suitable for complex shapes, and reduces post-processing.
- Disadvantages: High precision requirements for the model and higher mold costs.
- Applications: Examples include automotive parts, valve bodies, and pump bodies.
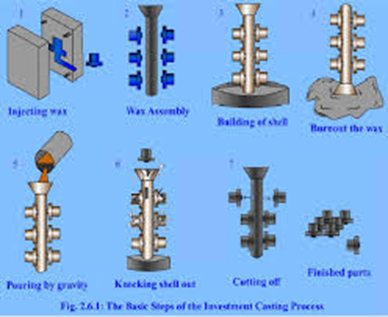
1.3 Precision Casting
Precision casting involves creating high-accuracy castings using wax or ceramic molds. It is often used for products requiring excellent surface quality and dimensional precision.
- Advantages: High accuracy and excellent surface quality, with minimal machining required
- Disadvantages: Higher cost and longer production cycles.
- Applications: Examples include aerospace components and high-end machinery parts
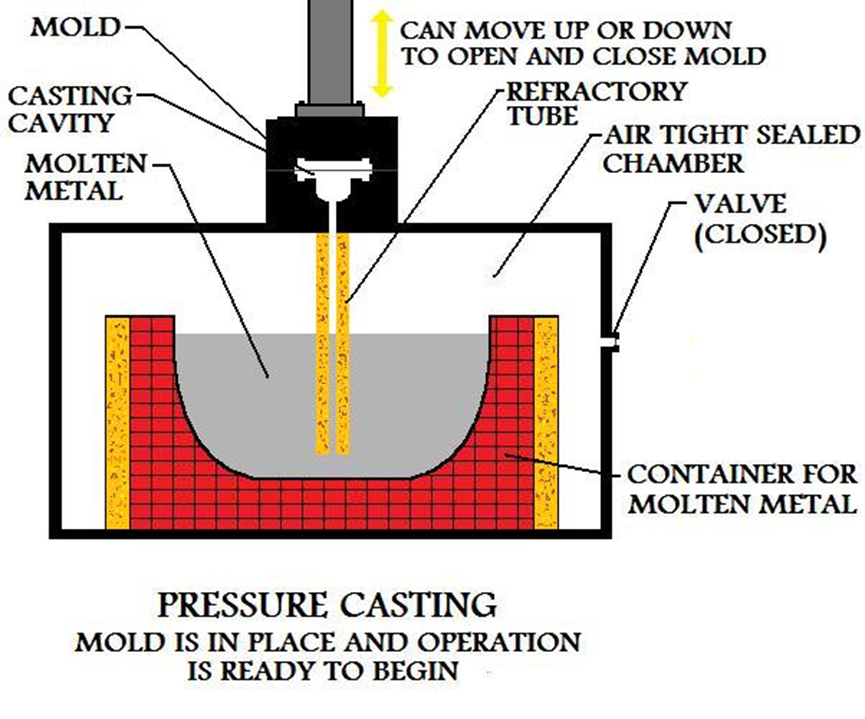
1.4 Pressure Casting
Pressure casting forces molten metal into a mold under high pressure for rapid shaping. This method is suitable for mass-producing small, lightweight components.
- Advantages: High production efficiency, ideal for large-scale manufacturing, and
uniform product quality.
- Disadvantages: High equipment investment and not suitable for large castings.
- Applications: · Examples include automotive components and electronic device housings.
 The most
common casting processes are the above ones. So how should we choose according
to our needs? Let's continue reading
The most
common casting processes are the above ones. So how should we choose according
to our needs? Let's continue reading
2. How to Choose a Cast Iron Casting Process
When selecting a casting process, multiple factors should be considered, including product design requirements, production costs, batch size, and specific application environments.
2.1 Based on Product Design Requirements
Complexity: For complex-shaped parts, consider lost foam casting or sand casting.
Dimensional Precision: For components with high precision and excellent surface quality requirements, precision casting is the best choice.
Wall Thickness: For thin-walled castings,
pressure casting is highly effective.
2.2 Based on Material Performance Requirements
Different types of cast iron (e.g., gray
iron, ductile iron, white iron) exhibit varying casting properties:
Gray iron is suitable for sand casting due
to its good fluidity and stable solidification.
Ductile iron works well with pressure or
precision casting, as it retains superior mechanical properties after forming.
2.3 Based on Production Cost and Scale
Small Batch Production: Sand casting is the
first choice due to its low mold cost and high flexibility.
Mass Production: Pressure casting is ideal
for its high efficiency, making it suitable for large-scale manufacturing.
2.4 Based on Industry Requirements
Automotive Industry: Pressure casting or
lost foam casting is often used to meet high strength and precision demands.
Construction Machinery: Sand casting is
commonly used due to its cost-effectiveness and versatility.
High-End Manufacturing: Precision casting
is preferred for aerospace or medical equipment components.
3. Future Developments in Cast Iron Casting Processes
With technological advancements, casting
processes are continually improving. For instance, the introduction of 3D
printing has made mold production more efficient and precise. Additionally,
environmental concerns are driving the development of greener processes, such
as techniques to reduce waste sand and gas emissions. These innovations make
casting process selection more diverse and offer manufacturers more
opportunities to optimize production.
Choosing the right cast iron casting
process is a crucial step in enhancing product quality and production
efficiency. Understanding the characteristics and applications of various
processes, combined with practical considerations, allows manufacturers to
optimize workflows, reduce costs, and meet customer needs. In the future, as
technology continues to advance, casting processes will become increasingly
intelligent and environmentally friendly, unlocking even greater potential for
industrial manufacturing.

 en
en  fra
fra  de
de  ru
ru  gle
gle  th
th  ara
ara  it
it  jp
jp  kor
kor  zh
zh 



