High Wear-Resistant Ductile Iron Castings Raw Materials and Chemical Composition Requirements
2025-01-20 16:10:42 hits:0
Raw Materials Suitable for High Wear-Resistant Ductile Iron Castings
To produce high wear-resistant castings, the raw materials used for ductile iron must possess high strength, hardness, and wear resistance. Achieving these properties often requires the use of specific alloying elements in ductile iron, optimizing the chemical composition and microstructure to enhance wear resistance. Below are the characteristics of raw materials suitable for high wear-resistant ductile iron castings and their chemical composition requirements.

Characteristics of Raw Materials Suitable for High Wear-Resistant Ductile Iron Castings:
- Pearlitic Matrix Structure: Pearlitic matrices have higher hardness and excellent wear resistance, making ductile iron with a pearlitic matrix structure more suitable for high wear-resistant castings.
- Graphite Spheroidization: The spheroidization of graphite significantly affects the mechanical properties and wear resistance of the casting. By controlling magnesium content and other alloying elements, spheroidization of graphite can be achieved, improving the toughness and wear resistance of the casting.
- Inclusion of Alloying Elements: Alloying elements (such as chromium, molybdenum, manganese, vanadium, etc.) significantly enhance the wear resistance of ductile iron. Choosing the right alloying elements is crucial for the wear performance of the casting.
Chemical Composition Requirements for High Wear-Resistant Ductile Iron
The raw materials for high wear-resistant castings typically need to meet certain chemical composition requirements, particularly in terms of alloying elements, to improve hardness, strength, and wear resistance. Below are the common chemical composition requirements for high wear-resistant ductile iron.
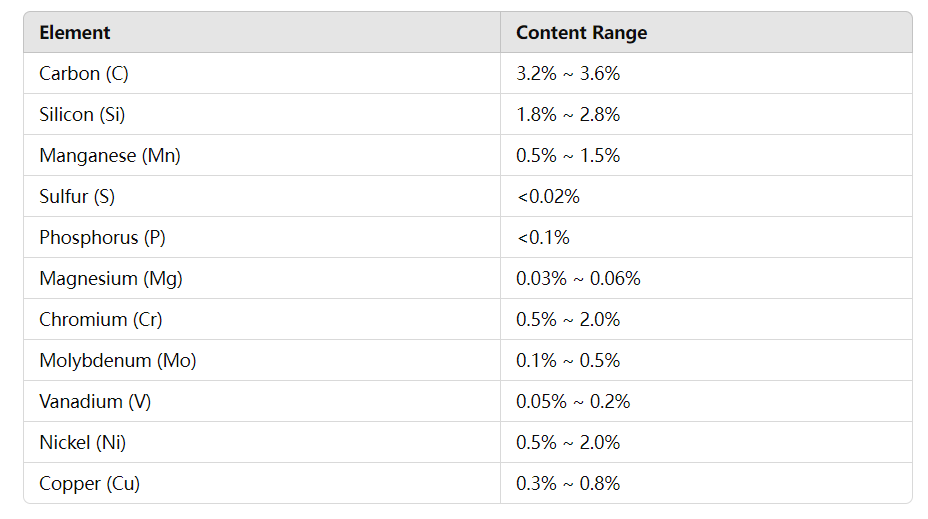
1. Carbon (C)
- Content Range: 3.2% ~ 3.6%
- Function: Carbon is the primary element in ductile iron, responsible for forming graphite nodules. Adequate carbon content helps increase the hardness and wear resistance of the iron.
2. Silicon (Si)
- Content Range: 1.8% ~ 2.8%
- Function: Silicon promotes the spheroidization of graphite, improving fluidity and enhancing wear resistance. Higher silicon content helps form a pearlitic structure, increasing hardness and wear resistance.
3. Manganese (Mn)
- Content Range: 0.5% ~ 1.5%
- Function: Manganese helps remove sulfur and oxygen impurities, increases the hardness and strength of the iron, and thereby enhances wear resistance. For high wear-resistant castings, increasing manganese content can significantly improve wear performance.
4. Sulfur (S)
- Content Requirement: < 0.02%
- Function: Sulfur is a harmful element that reduces wear resistance, strength, and toughness of ductile iron. The sulfur content in raw materials for high wear-resistant castings must be strictly controlled to improve the overall performance of the casting.
5. Phosphorus (P)
- Content Requirement: < 0.1%
- Function: Phosphorus is another harmful element that can reduce toughness. Excess phosphorus leads to brittle fractures. The phosphorus content in raw materials for high wear-resistant castings needs to be kept low to avoid compromising the mechanical properties.
6. Magnesium (Mg)
- Content Range: 0.03% ~ 0.06%
- Function: Magnesium is crucial in ductile iron to promote graphite spheroidization. Appropriate magnesium content helps improve toughness and strength, but for high wear-resistant ductile iron, it should be controlled to ensure even graphite distribution.
7. Chromium (Cr)
- Content Range: 0.5% ~ 2.0%
- Function: Chromium is a common alloying element used to enhance wear resistance. It increases hardness, strength, and corrosion resistance. Higher chromium content significantly improves wear resistance, especially in harsh wear conditions.
8. Molybdenum (Mo)
- Content Range: 0.1% ~ 0.5%
- Function: Molybdenum improves hardness and high-temperature performance. It enhances wear resistance under heavy load and friction conditions, making it effective for high wear-resistant castings.
9. Vanadium (V)
- Content Range: 0.05% ~ 0.2%
- Function: Vanadium enhances hardness and wear resistance by refining the grain structure. It is especially effective for castings subjected to high impact and friction.
10. Nickel (Ni)
- Content Range: 0.5% ~ 2.0%
- Function: Nickel improves corrosion resistance, toughness, and wear resistance. Increasing nickel content in high wear-resistant ductile iron can enhance its performance, especially in corrosive environments.
11. Copper (Cu)
- Content Range: 0.3% ~ 0.8%
- Function: Copper enhances both corrosion resistance and wear resistance. It is particularly effective for high wear-resistant castings exposed to wet or corrosive environments.
Summary of Chemical Composition for High Wear-Resistant Ductile Iron
|
|---|
Summary
To produce high wear-resistant ductile iron castings, the raw materials need to be precisely controlled in terms of chemical composition, especially the addition of alloying elements like chromium, molybdenum, manganese, and vanadium, which significantly enhance the hardness and wear resistance of the material. Adequate levels of carbon, silicon, and magnesium help improve mechanical properties, toughness, and the spheroidization of graphite, meeting the production requirements for high wear-resistant castings.

 en
en  fra
fra  de
de  ru
ru  gle
gle  th
th  ara
ara  it
it  jp
jp  kor
kor  zh
zh