Low Manganese Iron: Applications, Products, and Benefits
2024-12-27 13:56:21 hits:0
Low Manganese Iron refers to cast iron or alloy with a manganese content typically below 1%. Manganese in iron serves several purposes, such as sulfur removal, deoxidation, and improving the strength and hardness of steel and iron. However, high manganese content can negatively affect certain properties, particularly in applications requiring high weldability or low brittleness. Thus, low manganese iron finds its place in specific industries and applications.
Main Applications of Low Manganese Iron

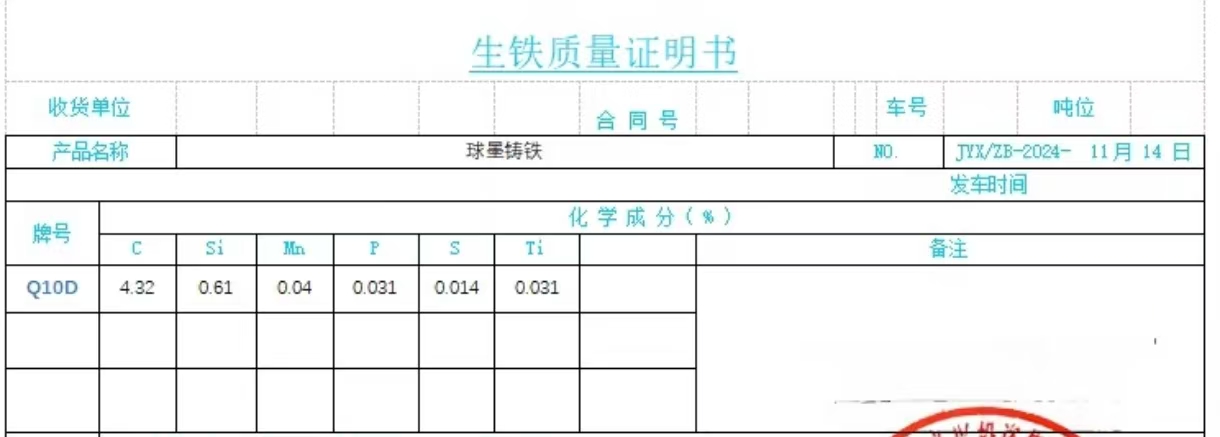
Low manganese iron is mainly used in the following sectors:
1. Casting Industry
Low manganese iron is widely used in casting, especially for manufacturing castings where low manganese content is required. Specific uses include:
- Gray Cast Iron: Low manganese iron is used in the production of gray cast iron, particularly when it's necessary to control the iron's toughness and weldability. Lower manganese content helps reduce brittleness, improving machinability and weldability.
- Ductile Cast Iron (Nodular Cast Iron): It can also be used in the production of ductile cast iron. By adjusting the manganese content, the strength and toughness of ductile iron can be optimized to meet different engineering requirements.
- Cast Steel Parts: Certain cast steel components may also use low manganese iron as a raw material, improving plasticity and elongation properties.
2. Steel Metallurgy
Low manganese iron can be used as an alloying element in steel production, especially in the manufacture of special steels that require lower manganese content:
- Tool Steels and High-Strength Steels: Some specialty tool steels or high-strength steels require lower manganese content to avoid negative effects on steel's brittleness and processing characteristics.
- Stainless Steel Production: In the production of some specific types of stainless steel, low manganese iron can be used to adjust the alloy's composition, improving its corrosion resistance and toughness.
3. Manufacturing Special Alloys
Low manganese iron is also used in the production of certain alloys, particularly those that require precise control of manganese content. Common applications include:
- Aluminum Alloys: In some aluminum alloy production processes, low manganese iron is used to adjust the manganese ratio, enhancing the alloy's strength and corrosion resistance.
- Copper Alloys: Certain copper-based alloys also use low manganese iron to improve mechanical properties and corrosion resistance.
4. Mechanical Manufacturing
Low manganese iron is sometimes used in the production of low manganese alloy steels and castings, particularly in applications that require high toughness and weldability, such as:
- Wheels, Bearings, Gears, and Other Mechanical Components: In mechanical manufacturing, certain parts require low manganese content to ensure the material's workability.
- Pressure Vessels and Piping: Some pressure vessel and pipeline materials may use low manganese iron to reduce the negative impact of manganese on steel's brittleness, especially in high-temperature and high-pressure environments.
Main Products of Low Manganese Iron
Low Manganese Cast Iron: This type of product features low manganese content in cast iron, typically used for producing castings that require high toughness and good machinability. Its main applications include automotive engine components, mechanical parts, and piping systems.
Low Manganese Steel: This steel is characterized by lower manganese content and is mainly used in the production of high-strength steels, which have good ductility and toughness. It's typically used in the manufacturing of bridges, ships, and pressure vessels.
Low Manganese Alloy Iron: This product is used in the production of specialty alloys, especially in aluminum, copper, and other alloys that require a controlled manganese composition.
Low Manganese Steel Plates/Pipes: Low manganese steel plates and pipes are widely used in construction, energy, and mechanical manufacturing industries, especially in applications that require high toughness, weldability, and corrosion resistance.

Advantages and Challenges
Advantages:
- Good Weldability: Low manganese iron typically has better weldability due to the lower manganese content, which reduces brittleness and crack formation during welding.
- Improved Machinability: With lower manganese content, the machinability of iron and steel is generally enhanced, making it suitable for manufacturing processes that require high precision.
- Better Toughness: In some cases, low manganese iron provides improved toughness, particularly for applications where high impact strength is needed.
Challenges:
- Strength and Hardness Control: Since manganese is a hardening element, low manganese iron usually has lower strength and hardness. This may require the addition of other alloying elements (such as silicon, chromium, nickel) to enhance material performance.
- Higher Costs: In certain applications, low manganese iron needs to be combined with other alloying elements, which may lead to higher production costs.

 en
en  fra
fra  de
de  ru
ru  gle
gle  th
th  ara
ara  it
it  jp
jp  kor
kor  zh
zh 



