Comparison of Principles and Advantages of Different Cast Iron Production Equipment
2024-12-16 13:55:14 hits:0
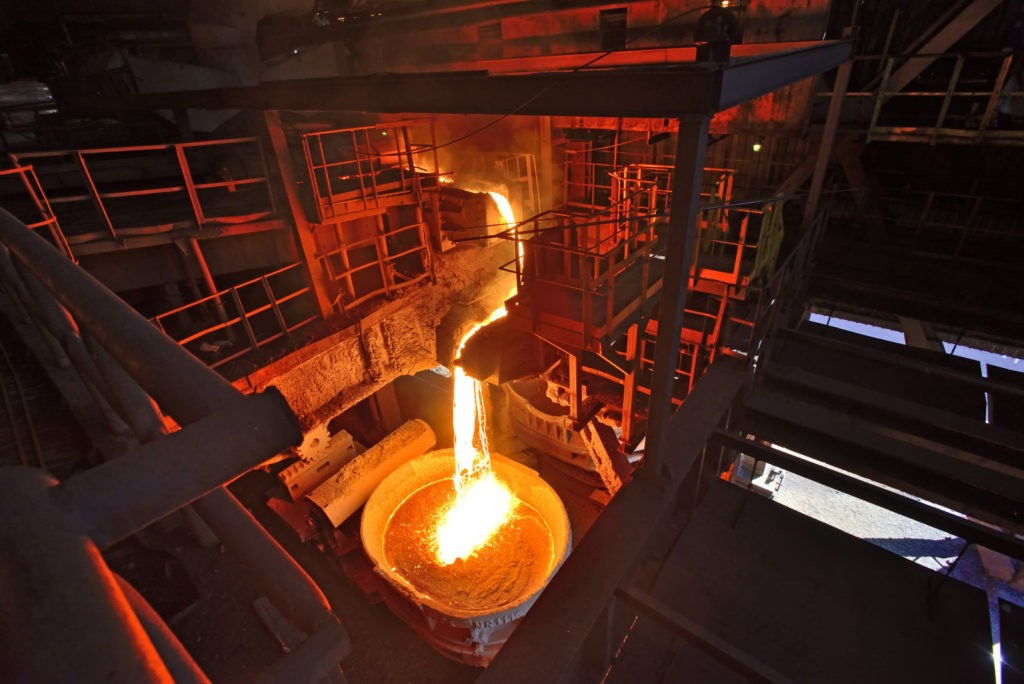

Cast iron is an important material widely used in industries such as engineering machinery, automotive, construction, and household appliances. The production of cast iron relies on various types of production equipment, and the choice of equipment directly impacts production efficiency, costs, and the quality of the final product. Different casting equipment operates on different production principles, each offering distinct advantages. Understanding these equipment's working principles and their pros and cons not only helps improve production efficiency but also optimizes processes and reduces costs. This article will provide a detailed comparison and analysis of the production principles and advantages of different cast iron production equipment.
Types of Cast Iron Production Equipment and Their Working Principles
Based on the production process and methods, cast iron production equipment can be categorized into several types: blast furnaces, electric furnaces, induction furnaces, and medium-frequency furnaces.
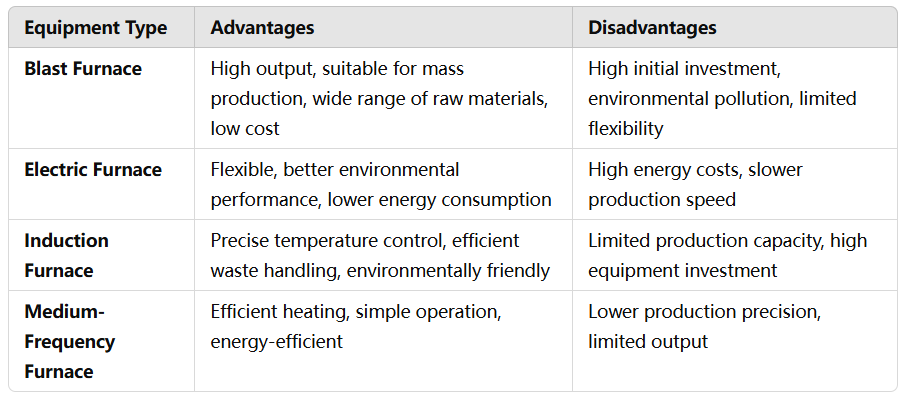
1. Blast Furnace
The blast furnace is one of the most traditional and commonly used devices in cast iron production. It works by heating raw materials such as iron ore, coke, and limestone to a high temperature inside the furnace, where chemical reactions reduce the iron ore to molten iron. Blast furnaces are mainly used for large-scale cast iron production, offering high production efficiency and relatively low unit energy consumption.
Advantages:
- High Output: Blast furnaces can operate continuously, making them ideal for mass production.
- Wide Range of Raw Materials: It can use iron ore, scrap steel, coke, and other materials.
- Lower Costs: Large-scale production helps spread fixed costs, lowering the unit cost of production.
Disadvantages:
- High Equipment Investment: Building and maintaining a blast furnace is expensive.
- Environmental Impact: Blast furnaces produce significant emissions, requiring effective waste gas and slag management.
- Limited Flexibility: It is more suitable for mass production and not ideal for small-batch or customized production.
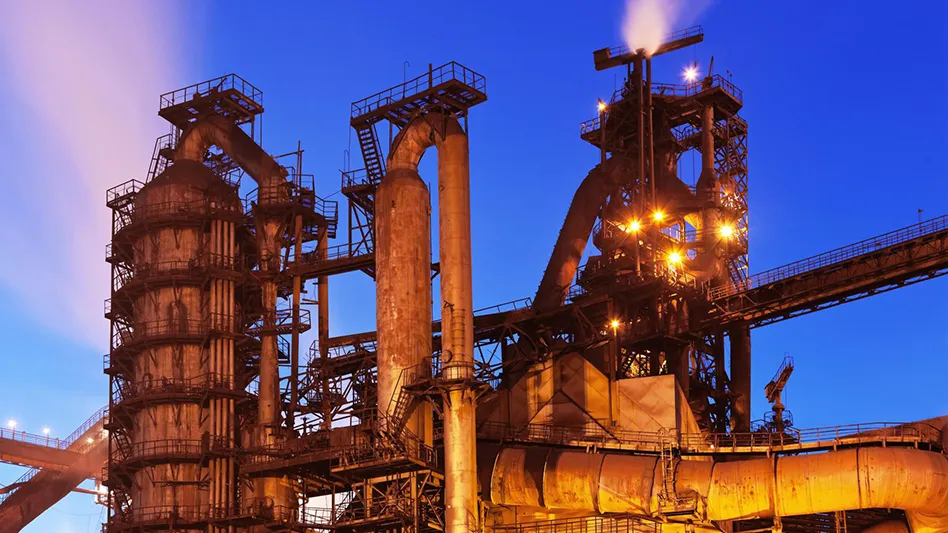

2. Electric Furnace
The electric furnace is a type of equipment that uses electricity as its primary heat source to melt scrap steel, iron chips, and other alloys. It is commonly used in medium to small-scale cast iron production, particularly for processing scrap iron and steel.
Advantages:
- Strong Flexibility: Suitable for medium- and small-batch production, and can produce various types of cast iron.
- Better Environmental Performance: Compared to blast furnaces, electric furnaces produce fewer harmful emissions.
- Lower Energy Consumption: Electric furnaces tend to be more energy-efficient than traditional methods.
Disadvantages:
- High Energy Costs: The operation of electric furnaces depends on electricity, and fluctuating electricity prices can impact production costs.
- Slower Production Speed: Compared to blast furnaces, electric furnaces have a longer production cycle.
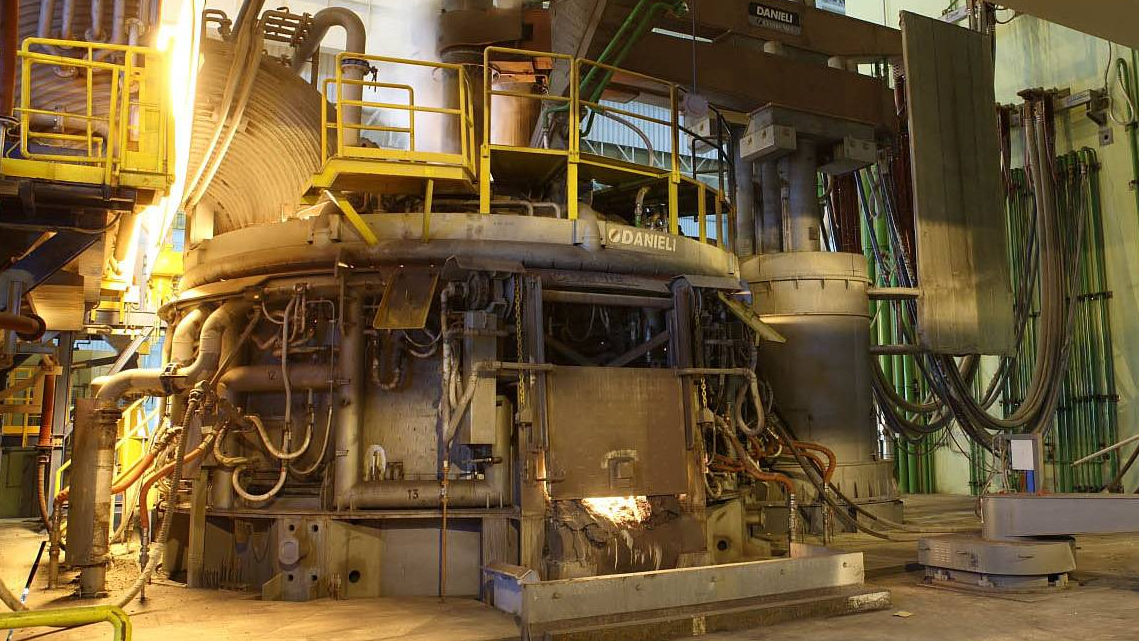

3. Induction Furnace
Induction furnaces operate using electromagnetic induction, which generates heat to melt metal. Induction furnaces are widely used for refining cast iron and alloying metals, and they are common in medium- to small-sized casting operations. This type of furnace allows for precise control over the melting process.
Advantages:
- Precise Temperature Control: Allows for accurate control of the melting temperature, ensuring consistent product quality.
- Efficient Waste Handling: Induction furnaces can efficiently process scrap metal.
- Better Environmental Performance: There is no combustion process, so waste gas emissions are minimal.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Production Capacity: Induction furnaces are better suited for medium- to small-scale production and are not ideal for large-volume production.
- Higher Equipment Investment: Induction furnaces require significant investment for setup and maintenance.
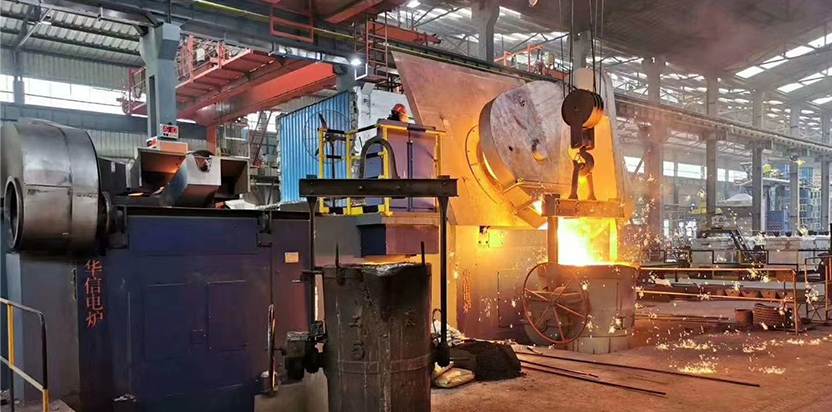

4. Medium-Frequency Furnace
Medium-frequency furnaces are similar to induction furnaces but use a medium-frequency power supply. They are typically used in steel and cast iron refining. Due to their lower frequency, they offer stronger heating capabilities, making them suitable for melting a variety of metals and alloys.
Advantages:
- Efficient Heating: Medium-frequency furnaces offer strong heating capabilities, making them suitable for melting large amounts of metal.
- Simple Operation: They are relatively easy to operate and maintain.
- Energy-Efficient: Medium-frequency furnaces have high energy efficiency and produce fewer emissions.
Disadvantages:
- Lower Production Precision: Compared to induction furnaces, medium-frequency furnaces offer less precise temperature control.
- Limited Output: The production capacity of medium-frequency furnaces is still lower than that of blast furnaces.

Comparison of Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Cast Iron Production Equipment
How to Choose the Right Cast Iron Production Equipment?
When selecting cast iron production equipment, it's essential to consider several factors, such as production needs, scale, product variety, and investment capacity.
- For large-scale production: If your business requires high-volume, standardized cast iron production, and uses relatively uniform raw materials, the blast furnace is the ideal choice.
- For medium to small-scale production: Electric furnaces and induction furnaces are better suited for flexible, small-batch production, especially when refining or alloying cast iron.
- For environmentally-conscious production: If minimizing emissions is a priority, electric furnaces and induction furnaces provide better environmental performance.
- For businesses with limited budgets: Medium-frequency furnaces are a cost-effective option for small to medium-sized enterprises, offering a balance of performance and investment.
Different cast iron production equipment has unique advantages and limitations, and choosing the right equipment depends on factors such as production needs, scale, and investment capacity. By understanding the production principles and pros and cons of each type of equipment, businesses can optimize their manufacturing processes, improve efficiency, and reduce costs. This knowledge is essential for staying competitive in today's fast-evolving industrial landscape.

 en
en  fra
fra  de
de  ru
ru  gle
gle  th
th  ara
ara  it
it  jp
jp  kor
kor  zh
zh 


