The Role and Design Requirements of the Differential Housing in Car Engines
2024-12-12 13:35:50 hits:0

The differential housing is a key component in a car's driveline system. While it may not receive as much attention as the engine or transmission, it plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth driving and power transmission. The differential housing not only protects the internal components of the differential but also performs important functions such as power distribution and load-bearing. In this article, we will explore the role, design requirements, and common materials used for differential housings in car engines, helping readers gain a comprehensive understanding of this essential automotive part.
The Basic Functions of the Differential Housing
The differential housing is typically located in the car's front or rear axle and serves several key functions:1.Protecting the Internal Components of the Differential
The primary function of the differential housing is to protect the internal gears and bearings of the differential. Since the gears inside the differential bear the torque from the engine, the housing must be strong enough to prevent damage and ensure smooth operation.2.Power Transmission
The differential housing houses the differential gears, which transmit power from the driveshaft to the left and right wheels. It ensures that the wheels rotate at different speeds when turning, maintaining stability and traction.3.Supporting and Sealing
The differential housing provides support for the bearings inside the differential and contains the space for the lubricant, preventing oil leakage and ensuring the lubrication system functions properly to extend the lifespan of the differential.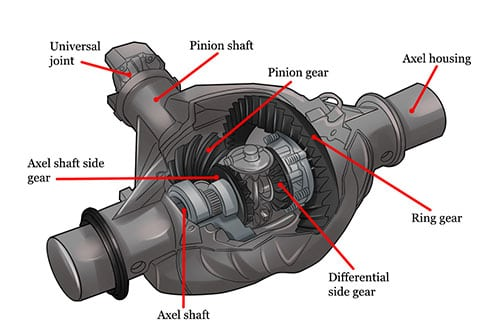
Common Materials for Differential Housings
The material used for the differential housing directly impacts its strength, weight, and durability. Common materials include:
1.Cast Iron
Cast iron is widely used for differential housings in traditional vehicles, particularly for cars that prioritize cost and weight. Cast iron has good casting properties, can withstand significant loads, and offers excellent wear resistance.
2.Aluminum Alloy
To meet the demands for lightweight and high-performance vehicles, some premium or sports cars use aluminum alloy for differential housings. Aluminum is lighter than cast iron, which helps improve fuel efficiency and vehicle handling performance.
3.Steel
In heavy-duty applications or for high-performance vehicles, differential housings may be made of steel, particularly for trucks or cars with high-powered engines. Steel offers higher strength and can withstand greater loads, making it suitable for demanding environments.
Design Requirements for Differential Housings
A differential housing must meet several design requirements to ensure it performs effectively and lasts a long time under varying conditions.1.High Strength and Durability
The differential housing must be able to withstand the torque from the engine and the immense pressure during operation. Its strength must be sufficient to prevent cracking or deformation under prolonged use. The material must also have good fatigue and impact resistance.2.Precision and Tolerance
The dimensions of the differential housing must be precise, especially in the areas where the differential gears and bearings are installed. Improper fit or dimensional errors can cause excessive wear, leading to poor performance and potential failure.3.Heat Dissipation and Cooling Design
Differentials generate significant heat during operation. Therefore, the housing design needs to address heat dissipation effectively. For example, some differential housings feature heat sinks or ventilation holes to help reduce the temperature and prevent overheating.4.Sealing and Lubrication System
Sealing is critical for maintaining the integrity of the lubrication system within the differential. A well-designed seal prevents oil leakage, ensuring that the differential remains properly lubricated, reducing wear, and extending the life of the system.Applications of Differential Housings
In addition to traditional front-wheel and rear-wheel-drive vehicles, differential housings are also used in four-wheel-drive (4WD) and all-wheel-drive (AWD) systems. In these vehicles, the differential housing plays a crucial role in distributing power to all four wheels, ensuring the vehicle maintains good traction and stability in various driving conditions, such as off-road or slippery terrains.
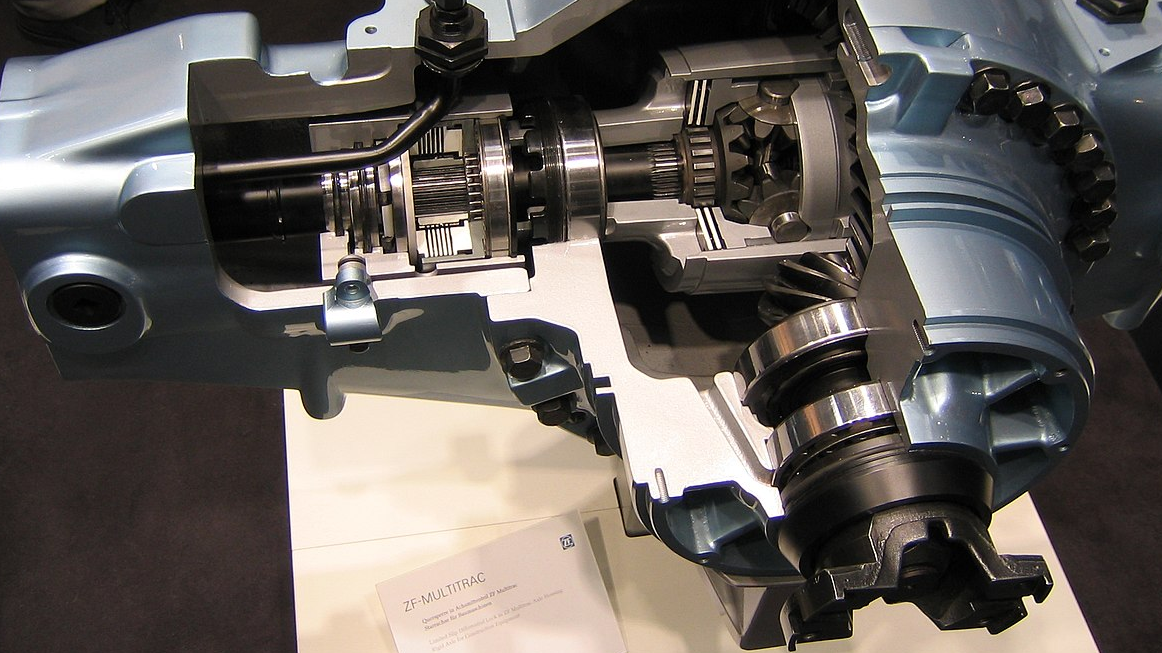
The differential housing is a vital component of a car's driveline system. It not only protects the internal gears and bearings of the differential but also plays an essential role in power transmission and smooth driving. Understanding the design requirements and material choices for differential housings helps us appreciate their importance in vehicle performance. We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of differential housings. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to contact us and we will get back to you within 24 hours.

 en
en  fra
fra  de
de  ru
ru  gle
gle  th
th  ara
ara  it
it  jp
jp  kor
kor  zh
zh 


