How to Distinguish Between Casting and Forging?
2024-12-11 15:56:49 hits:0
1.Definition of Casting and Forging
In manufacturing, casting and forging are two common metalworking processes with distinct techniques and applications. In simple terms, casting involves melting metal and pouring it into a mold to achieve the desired shape, while forging applies pressure to metal in its solid state to alter its shape and properties. Understanding the differences between these processes helps in selecting the most suitable method for specific product requirements.What is Casting?
Casting involves heating metal to a molten state and then pouring it into a pre-made mold to solidify into the desired shape. This process is suitable for producing complex shapes, especially components that are challenging to manufacture using other methods.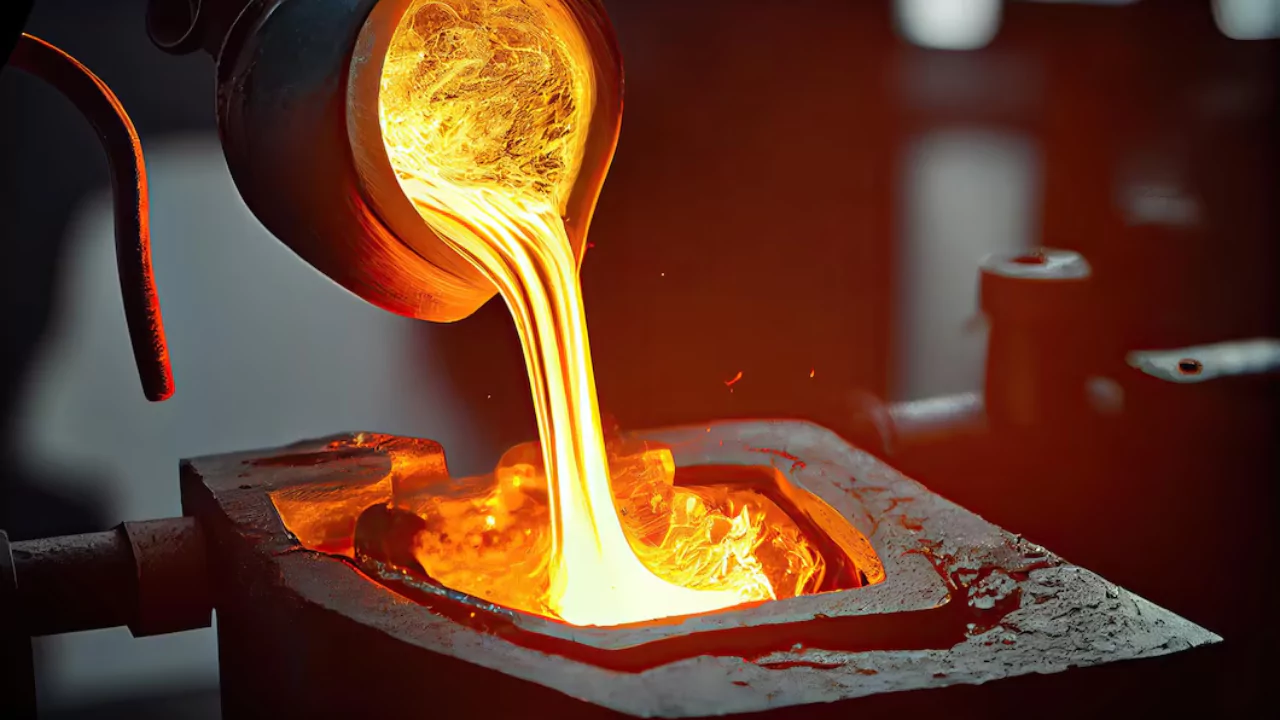
What is Forging?
Forging is a process of applying external force to metal, causing it to deform plastically in its solid state, thereby achieving a specific shape and mechanical properties. It is commonly used to manufacture parts with high strength and toughness, such as crankshafts and connecting rods in vehicles.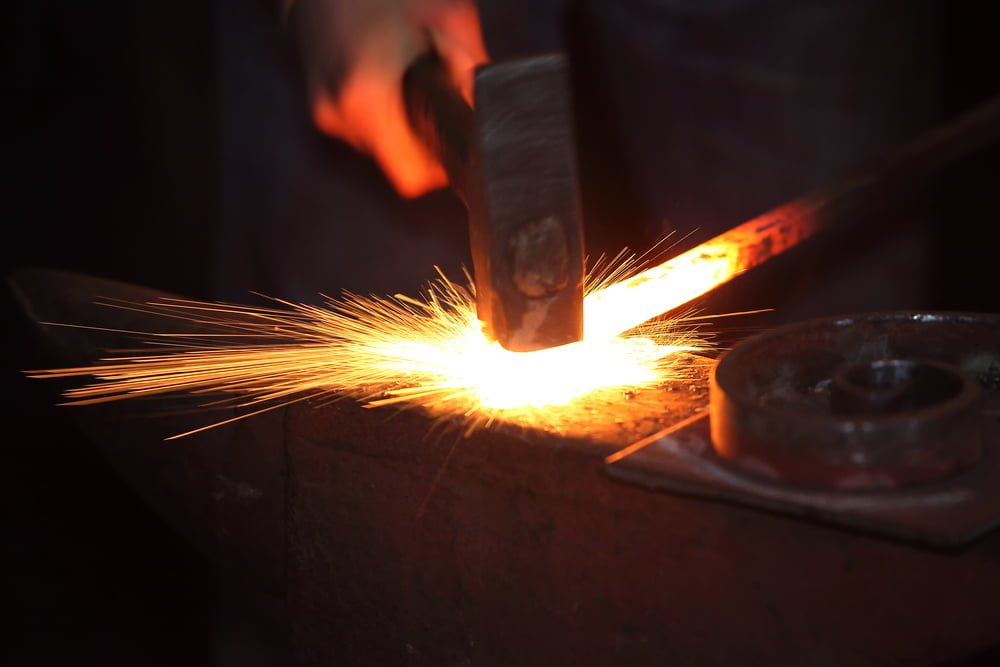
2.Differences Between Casting and Forging
While both casting and forging are used to manufacture metal parts, they differ significantly in terms of processing techniques, material characteristics, and the performance of the final product.2.1Processing Techniques
- Casting: The metal is melted and poured into a mold, then solidified into shape.
Characteristics: Suitable for making complex or large components.
- Forging: The metal is shaped by hammering, pressing, or squeezing under mechanical force.
Characteristics: Often used to produce high-strength parts.
2.2Material State
- Casting: The metal must be heated to a molten state.
- Forging: The metal remains in a solid state, typically heated to a temperature suitable for plastic deformation (hot forging).
2.3Product Performance
- Casting Products:
Advantages: Complex shapes, suitable for mass production, relatively low cost.
Disadvantages: Prone to internal defects like porosity and cracks, with lower strength and toughness.
- Forging Products:
Disadvantages: Not suitable for complex shapes, higher cost for molds and equipment.
2.4Application Areas
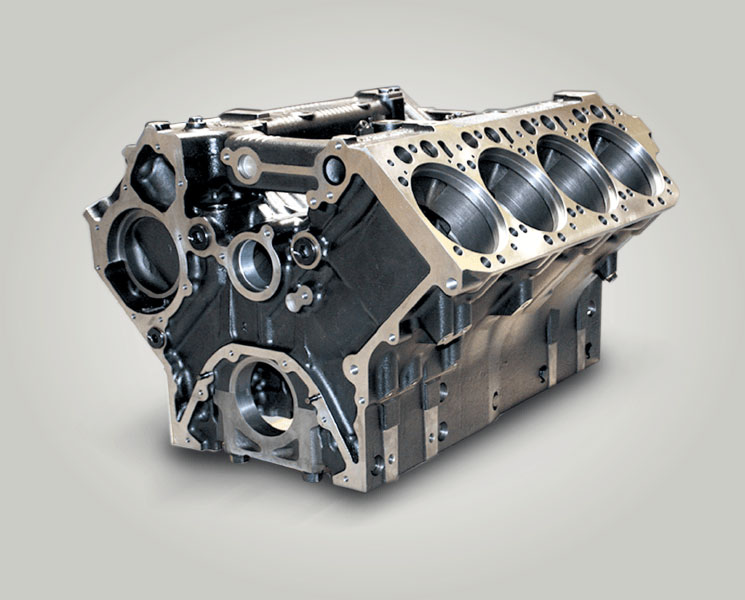
- Casting: Used in engine blocks, valves, pipe fittings, sculptures, etc.

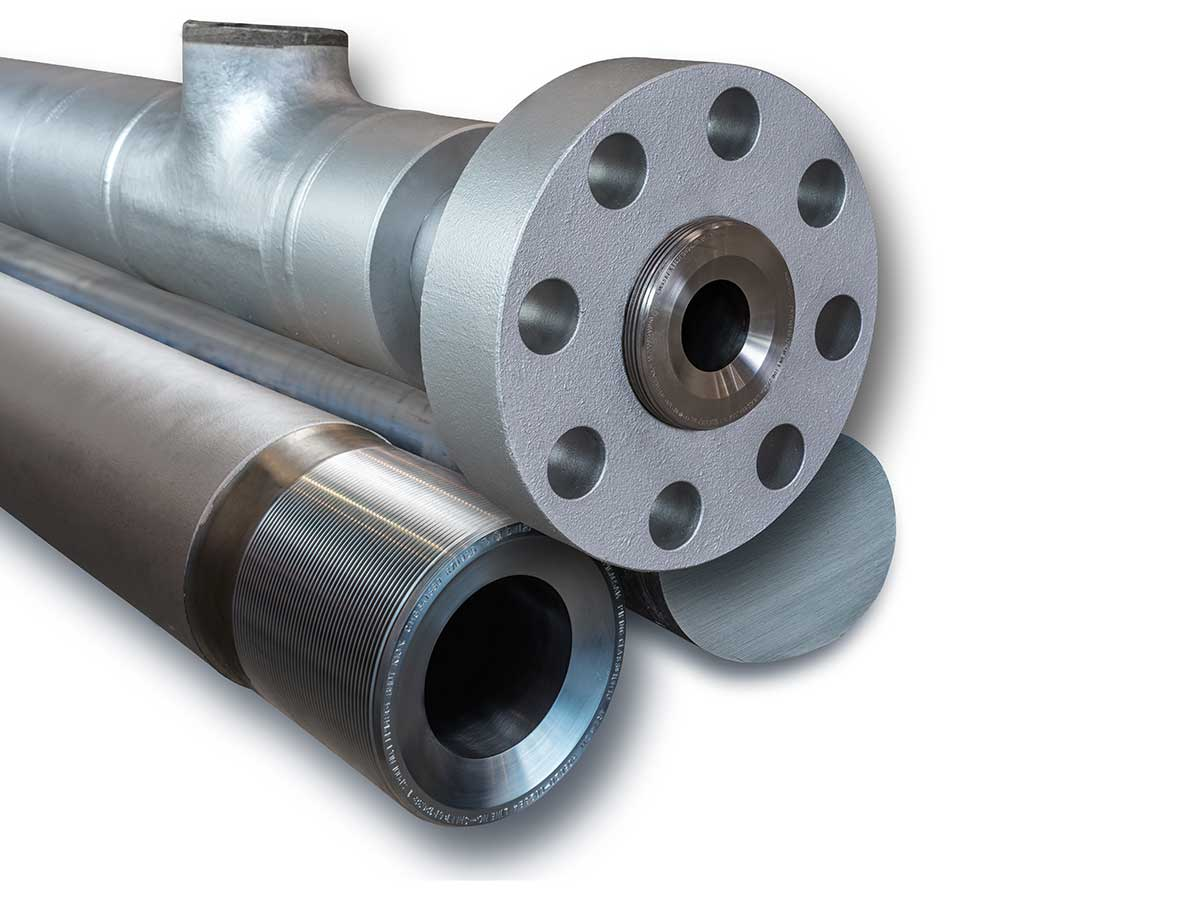
- Forging: Commonly applied to gears, shaft components, and high-pressure pipe joints that require high strength and toughness.

3.How to Choose Between Casting and Forging?
Selecting casting or forging depends on several factors:- Shape of the Part: Complex shapes are better suited for casting, while simpler but high-strength parts are better suited for forging.
- Performance Requirements: Parts requiring high strength and toughness are more suitable for forging.
- Production Cost: Casting is more cost-effective and ideal for mass production, whereas forging, though more expensive, ensures better product quality.
- Production Scale: Casting is commonly used for large-scale production of complex components, while forging is more appropriate for smaller-scale, high-performance part production.
Casting and forging are two essential processes in metalworking, each with its unique advantages and applications. Casting is characterized by its cost-effectiveness and ability to produce complex shapes, while forging is known for its superior strength and toughness. Understanding their differences and selecting the appropriate process based on requirements can better meet production and application demands.
We hope this article helps readers clearly understand the fundamental differences between casting and forging, providing valuable insights for material processing and part manufacturing.

 en
en  fra
fra  de
de  ru
ru  gle
gle  th
th  ara
ara  it
it  jp
jp  kor
kor  zh
zh 


